Choosing the right user research method
This job aid contains a list of different types of methods for performing design research, the characteristics and purpose of each type, as well as a chart describing what research method to adopt during the design process.
Purpose
To identify the types of research methods and choose the appropriate research methods during the entire research process.
Desired outcome
Selection of specific research methods for the design research, which leads to the effective and high-quality research.
When to use
Use this job aid at the planning stage of your design research.
Pairs well with
How to use
Using the following comparative tables and image, identify the types of research methods appropriate for your research goal and questions:
Research source
Research source
| Primary |
Secondary |
| Research that you conduct yourself by going directly to users |
Research previously gathered by and published by others |
| Resource-consuming |
Easier and quicker to obtain |
| Tailored to your specific needs |
Not as insightful |
Examples:
- Interviews
- Surveys
- Focus groups
|
Examples:
- Statistics published by government, non-government agencies, and trade bodies
- Company reports
- Textbooks and scholarly journals
- Online articles and research sites
|
Research method
Research method
| Qualitative |
Quantitative |
| Answer questions about why or how to fix a problem |
Answer questions about how many and how much |
| Collect users' statements |
Collect measurable data |
| Based on direct observation |
Collect data indirectly |
| Semi-structured |
Highly structured and standardize |
| Data are analyzed by categorization and interpretation |
Data are analyzed by statistical analysis |
| Might depend on the researcher's interpretation |
More objective (can be replicated) |
Note: Best practice: use a mix of both.
Best practice
Best practice
| Attitudinal |
Behavioural |
| Measure attitudes and beliefs (what people think they do) |
Measure behaviours (what people actually do) |
| Focus on how people think about a product |
Focus on action and performance |
| Rely on self-reported data |
Rely on observable data |
Note: Best practice: use a mix of both (for example, task analysis).
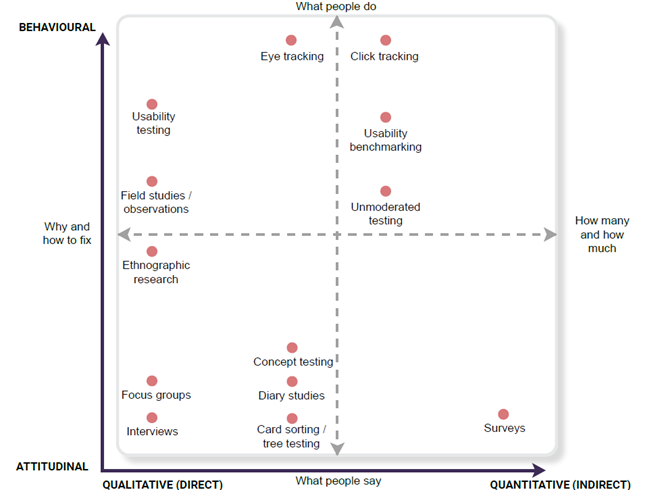
Research method landscape
Distribution of research methods across types of research.
Qualitative attitudinal research methods:
- Ethnographic research
- Focus groups
- Interviews
- Concept testing
- Diary studies
- Card sorting
- Tree sorting
Quantitative attitudinal research methods:
Qualitative behavioural research methods:
- Field studies
- Observations
- Eye tracking
- Usability testing
Quantitave behavioural research methods:
- Click tracking
- Usability benchmarking
- Unmoderated testing
- User behaviour testing
- A/B testing
Choosing research methods at different stages of the design process
Using the following chart, identify the appropriate research methods for your research based on the research stage you are at:
Different stages of the design process
Different stages of the design process
| You are starting out |
Goal
To understand your users and the underlying problem
Methods
Mixture of both qualitative and quantitative methods, such as field studies, diary studies, surveys, and data mining
|
| You have established a direction for your design |
Goal
To evaluate your designs and make sure that they adequately address your users' needs
Methods
Research methods that help you to optimize your designs and improve usability, such as card sorting and usability testing
|
| You have finalized your design and developed a working product |
Goal
To investigate how well the product performs in the real world
Methods
Mainly quantitative research methods, such as usability benchmarking, surveys, and A/B testing
|
Source: Visit A Guide to Using User-Experience Research Methods for more information.